A proportional valve adjusts its valve opening continuously based on an input signal (usually a voltage or current, such as 0–10 V or 4–20 mA).
The higher the input signal, the more the valve opens; the lower the signal, the more it closes.
In simple terms:
Electrical signal → proportional valve movement → controlled flow or pressure
This makes proportional valves ideal for applications that require smooth, accurate, and variable control.
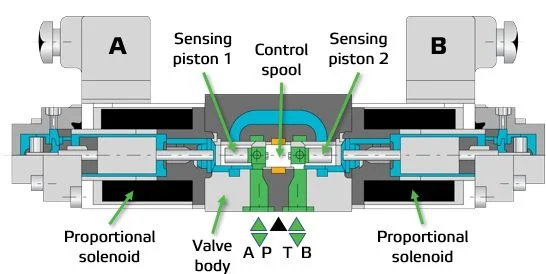
Table of Contents
ToggleHow Does a Proportional Valve Work?
A proportional valve typically consists of:
Solenoid or proportional actuator
Valve spool or poppet
Electronic driver (amplifier)
Working principle:
A controller sends an electrical signal
The proportional solenoid converts the signal into magnetic force
The valve spool moves partially, not just on/off
Fluid flow or pressure changes proportionally
Unlike standard solenoid valves, the spool position is continuously adjustable.
Proportional Valve vs On/Off Valve
| Feature | Proportional Valve | On/Off Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Control type | Variable / continuous | Binary (open or closed) |
| Precision | High | Low |
| Motion | Smooth | Sudden |
| Energy efficiency | Better in many systems | Lower |
| Typical signal | Analog (0–10V, 4–20mA) | Digital (0 or 1) |
Types of Proportional Valves
1. Proportional Flow Control Valve
Regulates flow rate
Used to control speed of actuators
2. Proportional Pressure Control Valve
Controls system pressure
Includes pressure-reducing and relief variants
3. Proportional Directional Control Valve
Controls direction and speed
Common in hydraulic machinery
Applications of Proportional Valves
Proportional valves are widely used in industries that require precise motion and force control, such as:
Hydraulic machinery
Injection molding machines
Construction equipment
Industrial automation
Wind power systems
Robotics
Marine and offshore equipment
Advantages of Proportional Valves
Precise control of flow and pressure
Smooth system operation
Reduced mechanical shock
Improved energy efficiency
Easy integration with PLCs and controllers
Limitations to Consider
More expensive than on/off valves
Sensitive to fluid contamination
Requires proper electronic control and tuning
Proportional Valve vs Servo Valve
| Aspect | Proportional Valve | Servo Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | High | Very high |
| Cost | Moderate | Expensive |
| Contamination tolerance | Better | Poor |
| Complexity | Lower | Higher |
Proportional valves are often chosen as a cost-effective alternative to servo valves.
Conclusion
A proportional valve is a key component in modern hydraulic and pneumatic systems, enabling precise, smooth, and efficient control of fluid flow or pressure based on electrical signals.
If your application needs variable control instead of simple on/off operation, a proportional valve is usually the right choice.
